Pratenséine
La pratenséine est un composé organique de la famille des isoflavones O-méthylées, un type de flavonoïde. Elle est notamment présente dans le trèfle des prés (Trifolium pratense)[2]. Elle pourrait avoir un effet préventif contre l'athérosclérose[3].
| Pratenséine | |
| |
| Identification | |
|---|---|
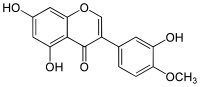
| Nom UICPA | 5,7-dihydroxy-3-(3-hydroxy-4-méthoxyphényl)chromén-4-one |
| Synonymes |
4'-méthoxy-3',5,7-trihydroxyisoflavone |
| No CAS | |
| PubChem | 5281803 |
| SMILES | |
| InChI | |
| Propriétés chimiques | |
| Formule | C16H12O6 [Isomères] |
| Masse molaire[1] | 300,262 9 ± 0,015 4 g/mol C 64 %, H 4,03 %, O 31,97 %, |
| Unités du SI et CNTP, sauf indication contraire. | |
Notes et références
- Masse molaire calculée d’après « Atomic weights of the elements 2007 », sur www.chem.qmul.ac.uk.
- Isoflavone contents of red and subterranean clovers. E. Wong, Journal of the Science of Food and Agriculture, Volume 14 Issue 6, Pages 376-379
- Characterization of the Isoflavone Pratensein as a Novel Transcriptional Up-Regulator of Scavenger Receptor Class B Type I in HepG2 Cells. Yang Yuan, JIiang Wei, Wang Li, Hang Zhong-Bing, Si Shu-Yi and Hong Bin, Biological & pharmaceutical bulletin, 2009, vol. 32, no7, pp. 1289-1294
- Portail de la chimie
Cet article est issu de Wikipedia. Le texte est sous licence Creative Commons – Attribution – Partage à l’identique. Des conditions supplémentaires peuvent s’appliquer aux fichiers multimédias.