Homobatrachotoxine
L'homobatrachotoxine est un alcaloïde stéroïdien.
| Homoatrachotoxine | ||
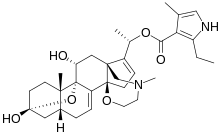 | ||
| Structure de l'homobatrachotoxine. | ||
| Identification | ||
|---|---|---|
| No CAS | ||
| SMILES | ||
| InChI | ||
| Propriétés chimiques | ||
| Formule | C32H44N2O6 [Isomères] |
|
| Masse molaire[1] | 552,701 6 ± 0,030 9 g/mol C 69,54 %, H 8,02 %, N 5,07 %, O 17,37 %, |
|
| Écotoxicologie | ||
| DL50 | >0,003 mg·kg-1 (souris, i.p.) [2] | |
| Unités du SI et CNTP, sauf indication contraire. | ||
Notes et références
- Masse molaire calculée d’après « Atomic weights of the elements 2007 », sur www.chem.qmul.ac.uk.
- (en) « Homobatrachotoxine », sur ChemIDplus, consulté le 13 mai 2011
- (en) « Homobatrachotoxine », sur ChemIDplus.
- Portail de la chimie
- Portail de la pharmacie
Cet article est issu de Wikipedia. Le texte est sous licence Creative Commons – Attribution – Partage à l’identique. Des conditions supplémentaires peuvent s’appliquer aux fichiers multimédias.