2-C-Méthylérythritol-4-phosphate
Le 2-C-méthylérythritol-4-phosphate (MEP) est un intermédiaire de la voie du méthylérythritol phosphate (voie « non mévalonique ») de biosynthèse des isoprénoïdes.
| 2-C-Méthylérythritol-4-phosphate | |
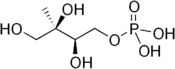 Structure du 2-C-méthylérythritol-4-phosphate |
|
| Identification | |
|---|---|
| Nom UICPA | [(2R,3S)-2,3,4-trihydroxy-3-méthylbutyl] dihydrogénophosphate |
| No CAS | |
| PubChem | 443198 |
| ChEBI | 17764 |
| SMILES | |
| InChI | |
| Propriétés chimiques | |
| Formule | C5H13O7P [Isomères] |
| Masse molaire[1] | 216,126 3 ± 0,007 g/mol C 27,79 %, H 6,06 %, O 51,82 %, P 14,33 %, |
| Unités du SI et CNTP, sauf indication contraire. | |
Notes et références
- Masse molaire calculée d’après « Atomic weights of the elements 2007 », sur www.chem.qmul.ac.uk.
- Portail de la chimie
- Portail de la biochimie
Cet article est issu de Wikipedia. Le texte est sous licence Creative Commons – Attribution – Partage à l’identique. Des conditions supplémentaires peuvent s’appliquer aux fichiers multimédias.